Consultant Hand & Reconstructive Microsurgeon at Medicare Hospital & Research Centre, Old Palasia, Indore.

1. M.B.B.S. from MGM medical College, Indore (2001 - 2006).
2.MS (Orthopaedics) from GMC, Bhopal
3.Registrar, Orthopaedics at ApolloHospital, New Delhi, India(JCI Accredited)(June-July2010)
4.Hand and Microsurgery trainee at Poona Hand Surgery, Pune, India (March-June 2011), under Dr Pankaj Jindal (Hand and Microsurgery fellow, Louisville & Hand Surgery fellow, France)
5.Clinical fellow in Hand & Reconstructive Microsurgery at Ganga Hospitals, Coimbatore , India (Aug.2011-July2012: 1 year)

1. MP-UP Exchange Fellowship 2010 for Second Best PG Paper at the Joint Annual Conference of Central Zone and MP Chapter IOA, held at Bhopal, Oct.30-Nov.1, 2009
2. Dr. Rajeev Rallan Memorial Gold Medal for securing overall first position in Orthopaedics, 2006
3. Gold Medal for overall first position in III Prof. part1 MBBS , 2005
4. Gold Medal for overall first position in Ophthalmology, 2005
5. Gold Medal for overall first position in Community Medicine, 2005
6. K.C. Rishi Memorial Gold Medal in Ophthalmology, 2005
7. Certificate and Cash Prize for securing overall 2nd position in Madhya Pradesh state in Medical Entrance Examination, 2001

1.Hand surgery course during APSICON Plastic surgery annual conference 2011 held at Coimbatore, Sep.2011
2.Poona Orthopaedics Society Comprehensive Hand Surgery Review Course, held at Pune, May 19, 2011
3.Rational use of blood and blood products”- Training Course for clinicians, held at GandhiMedicalCollege, Bhopal, Mar.22, 2010
4.“Indore Arthroplasty Course 2010”- Workshop on Total Knee Replacement, held at Indore, Mar.20-21, 2010
5.Orthopaedic Research and Education Foundation- India: National Post Graduate Instructional Course 2010, held at Indore, Jan.14-17, 2010
6.National Postgraduate Training Course held at Miraj, Sep. 5-6, 2009
7.AO Principles Pre-basic Course held at Miraj, Sep. 3-4, 2009
8.Workshops on PHN, ETN, TRAFON and DFN at National Conference of Interlocking Surgeons, NAILSCON 2009, Khajuraho, Oct.2, 2009
9.National PG Instruction Course held at Bhopal, Aug. 15-17, 2008
10.Workshop on Problem Solving for Better health (PSBH), held at MGMMedicalCollege, Indore, Sep.2004
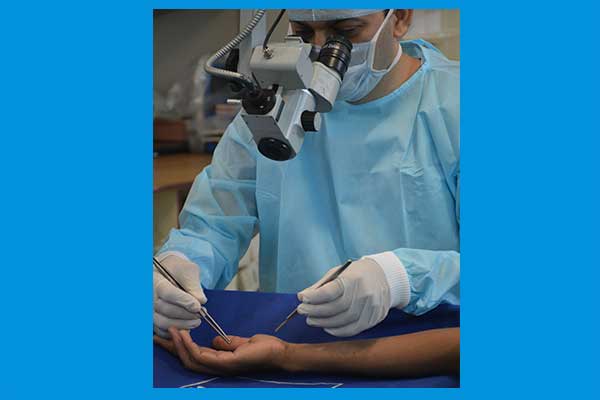
Hand and Wrist surgery, reconstructive microsurgery
The hand consists of 27 bones(including the 8 bones of the wrist).
When the other associated structures (nerves, arteries, veins, muscles, tendons, ligaments, joint cartilage and fingernails) are considered,the potential for a variety of injuries exists when trauma involves the hand.
Crush injuries are common in car accidents, falls and in any situation that can lead to a structure collapsing. But there are also varying degrees of crush injuries.
Subsequent swelling of the palmar structures further impairs venous outflow,and hemorrhage into structural spaces increases the pressure.
Replantation aims to restore the amputated part to its anatomical site, preserving function and appearance. Outcome depends on factors intrinsic to the patient and to the nature of the injury.Young patients who have distal, cleanly amputated extremities have the best return of function.
The technical steps involved include examination and dissection of the neurovascular structures, bone fixation, tendon and muscle repair followed by microsurgical artery, nerve and vein repair, and finally skin closure.
Hand contracture is a fairly common disorder of the fingers. that causes the tissue beneath the surface of the fingers to thicken and contract.
Once this occurs, the fingers affected by hand contracture can't be straightened completely, which can complicate everyday activities such as placing your hands in your pockets, putting on gloves or shaking hands.
Hand defects are common. Sometimes a hand does not form completely, and part or all of the hand may be missing. For example, the person may have too few fingers. Sometimes a hand does not develop. For example, the fingers may not separate, producing a weblike hand.
The little fingers or thumbs are most commonly duplicated. Overgrowth may occur, in which the hands or individual fingers are too large. Surgery is usually done to correct the hand defect and provide as much function as possible.
The ulnar nerve is one of the three main nerves that provide feeling and function to the hand it passes through a tunnel in the wrist called Guyon's canal.
Its symptoms include pain, tingling, numbness, and muscle weakness. The symptoms affect just one particular part of the body, depending on which nerve is affected.
Tendon transfer surgery is a type of hand surgery that is performed in order to improve lost hand function.
Nerve grafts are used when a patient has a nerve injury resulting in complete loss of muscle function or sensation.A nerve graft is a surgical technique in which a segment of unrelated nerve is used to replace or bridge an injured portion of nerve.
The donor nerve serves as a “track” along which axons (appendages of neurons, which transmit impulses from the spinal cord to the muscle) can grow down to the target area.
Reconstructive microsurgery is a surgical field where specialized operating microscopes and precision instrumentation are utilized to perform intricate operations on tiny structures.
The ability to reestablish continuity and blood flow to small, severed nerves and vessels has made a major impact on the potential to restore form and function to individuals impaired by trauma, cancer and congenital differences.
Reconstructive microsurgery has witnessed major advancements in the last decade including the emergence of hand and face transplantation.These techniques are providing a new lease on life for severely injured patients whose problems cannot be solved by more traditional techniques.
Nerve injury can be defined as a defect that results in a disruption of a nerve such that it can no longer transmit an action potential.
Microsurgery is surgery performed under the magnification of a microscope. Microsurgery makes it possible to reattach fingers, toes, hands and the performance of free tissue transplants and nerve repairs. A free-tissue transplant often includes skin and fatty tissue, bone, muscle and nerves.
Arthritis is a general term for inflammation in the joints, can occur in numerous forms. The hand and wrist have multiple small joints that work together to produce motion. The most common is osteoarthritis, a condition in which the cartilage, the protective cushioning between the joints, wears out.
When this happens, the bones rub directly against other bones. This causes structural changes that can be seen on X-rays.
When the joints are affected by arthritis, activities of daily living can be difficult for example the fine motion needed to thread a needle or tie a shoelace become harder.
The movement and power of your hand and wrist are controlled by muscles and tendons. Arthritis in the wrist joint is common in people with rheumatoid arthritis. Some people may need an operation if the joint is very painful and not responding to other treatment.
Finger deformities are common in persons with rheumatoid arthritis. A number of different disorders may affect the hands or fingers, including ganglia, deformities, disorders related to nerves or blood vessels, osteoarthritis, trigger finger, and infections.
Hand and finger deformities include swan-neck deformity , boutonnière deformity , and Dupuytren contracture . These deformities may be caused by an injury or may result from another disorder .
A method of thumb reconstruction with the thumb metacarpal intact.The advantage of the procedure is that the soft tissues covering the thumb are not disturbed thus preserving its sensibility. This method may be used when the thumb metacarpal is available and the skin is in good condition.